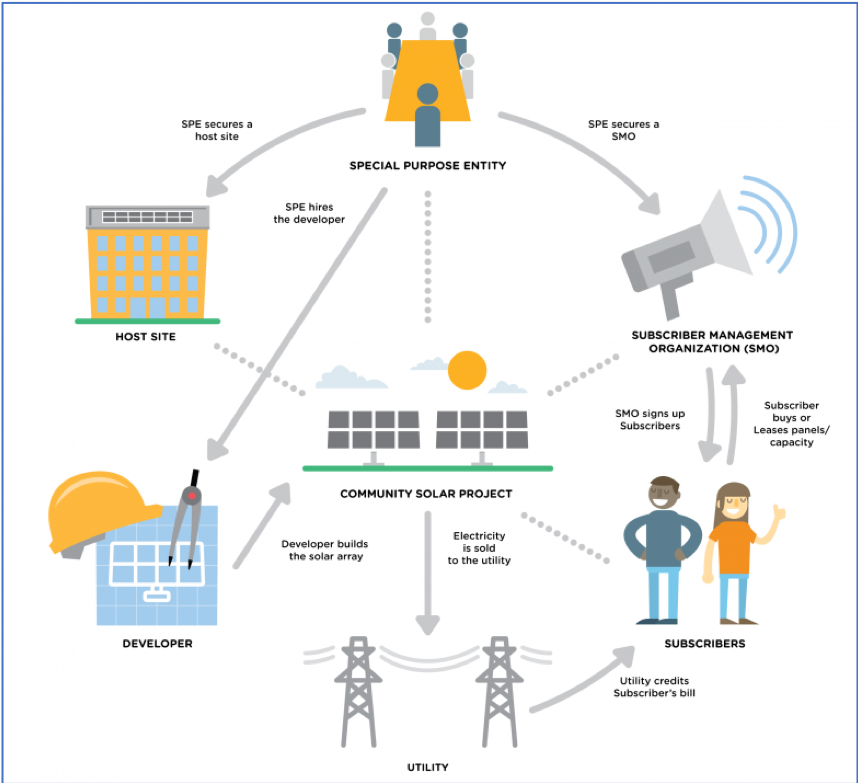
Most people in the United States are unable to access residential photovoltaic solar arrays (solar PV) due to the cost of installations, lack of building/home ownership and inadequate infrastructure. These challenges led to community solar (CS) and community shared solar (CSS) emerging as solutions that allow more people to access solar energy.
This study uses lessons learned from working with a Brooklyn, New York City-based community organization to determine the value propositions for three stakeholders critical to the community solar sector: (1) community groups, (2) solar developers and (3) solar investors through interviewing experts in the field.
The findings suggest that community groups are likely to value more than just the utility bill savings, developers find value in building relationships with communities to create more projects and investors are chiefly interested in taking advantage of income tax credits and depreciation benefits of community solar projects. While there is a great opportunity to build on this work, this study reveals some of the motivations of key stakeholders and provides insights that can be shared among all the stakeholders active in the community solar sector.
This is the student capstone project of Michael Harrington.